
In this tutorial, we will build Spring Boot CRUD REST API Project using IntelliJ IDEA as our IDE. We will use the Postman client to test the REST APIs. We will use Spring Data JPA to develop a repository layer and MySQL database at the backend.
Spring Boot provides a web tool called Spring Initializer to bootstrap
an application quickly. Just go to https://start.spring.io/ and
generate a new spring boot project.
Use the below details in the Spring boot creation:
Project Name: springboot-backend
Project Type: Maven
Choose dependencies: Spring Web, Lombok, Spring Data JPA, and MySQL Driver
Package name: net.javaguides.springboot
Packaging: Jar
Download Spring Boot project as a zip file, unzip it, and import it into IntelliJ IDEA.
Here is the pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-backend</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-backend</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot REST APIs</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
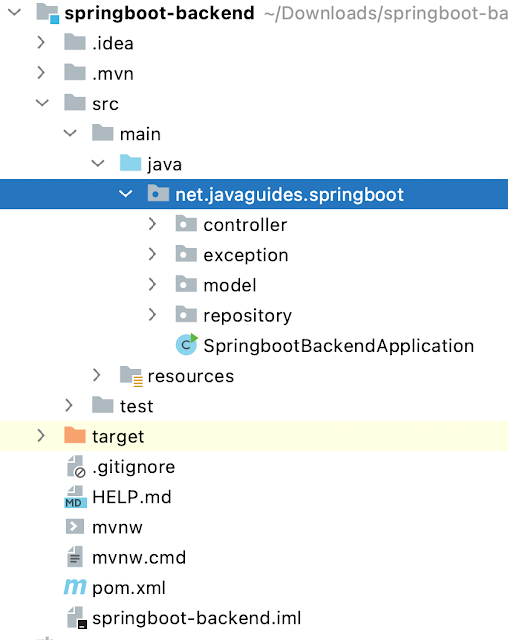
You below screenshot to create a project or packaging structure for your Spring boot project:
Since we’re using MySQL as our database, we need to configure the database URL, username, and password so that Spring can establish a connection with the database on startup. Open src/main/resources/application.properties file and add the following properties to it:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ems?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
Don’t forget to change the spring.datasource.username andspring.datasource.password
as per your MySQL installation. Also, create a database named ems in MySQL before proceeding to the next
section.
You don’t need to create any tables. The tables will automatically be created by Hibernate from the
Employee entity that we will define in the next step. This is made possible by the property
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update.
Go to model package, create a class named Employee and add the following content into it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email_id")
private String emailId;
}No, we gonna create a Spring Data JPA repository to talk with the MySQL database.
Go to repository package, create the following EmployeeRepository interface and
add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository {
// all crud database methods
}
Go to an exception package, create a class named ResourceNotFoundException and add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException{
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message){
super(message);
}
}Go to controller package, create a class named EmployeeController and add the following content to it:
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.EmployeeRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@CrossOrigin("*")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/employees")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@GetMapping
public List getAllEmployees(){
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
// build create employee REST API
@PostMapping
public Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
// build get employee by id REST API
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity getEmployeeById(@PathVariable long id){
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id:" + id));
return ResponseEntity.ok(employee);
}
// build update employee REST API
@PutMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity updateEmployee(@PathVariable long id,@RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) {
Employee updateEmployee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id: " + id));
updateEmployee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());
updateEmployee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());
updateEmployee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());
employeeRepository.save(updateEmployee);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updateEmployee);
}
// build delete employee REST API
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity deleteEmployee(@PathVariable long id){
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id: " + id));
employeeRepository.delete(employee);
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
}
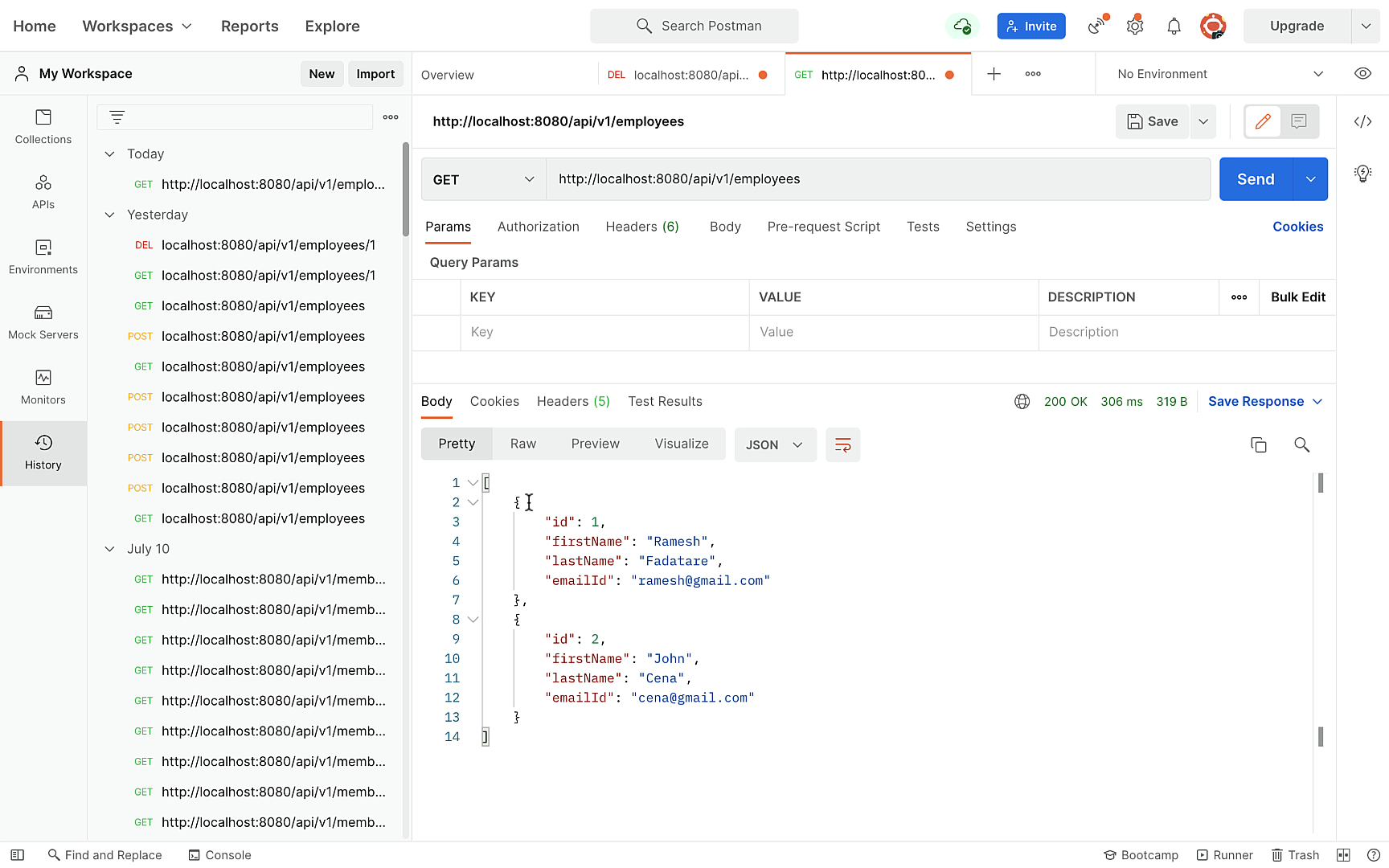
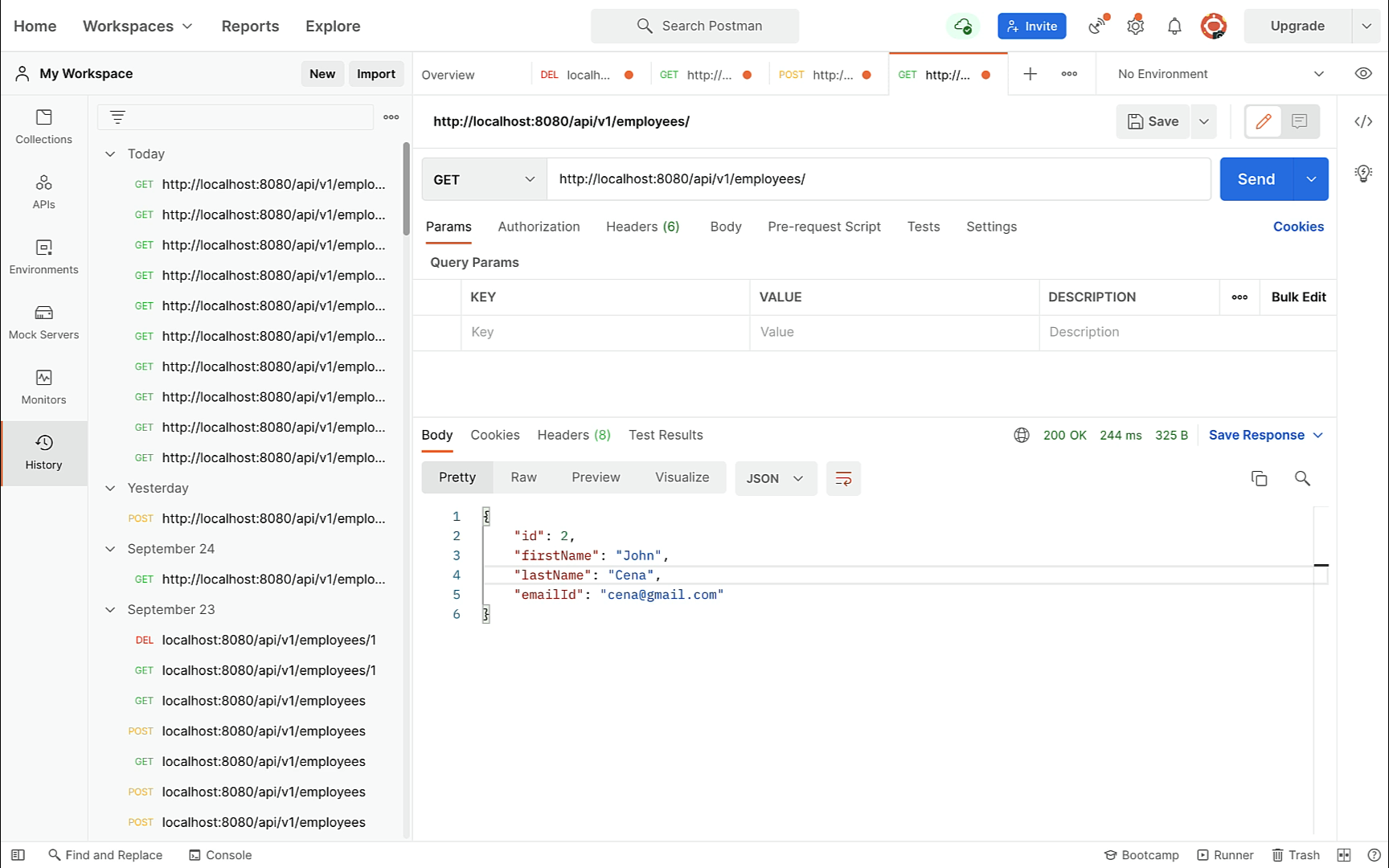
} Get All Employees REST API:
@GetMapping
public List getAllEmployees(){
return employeeRepository.findAll();
} Create Employee REST API:
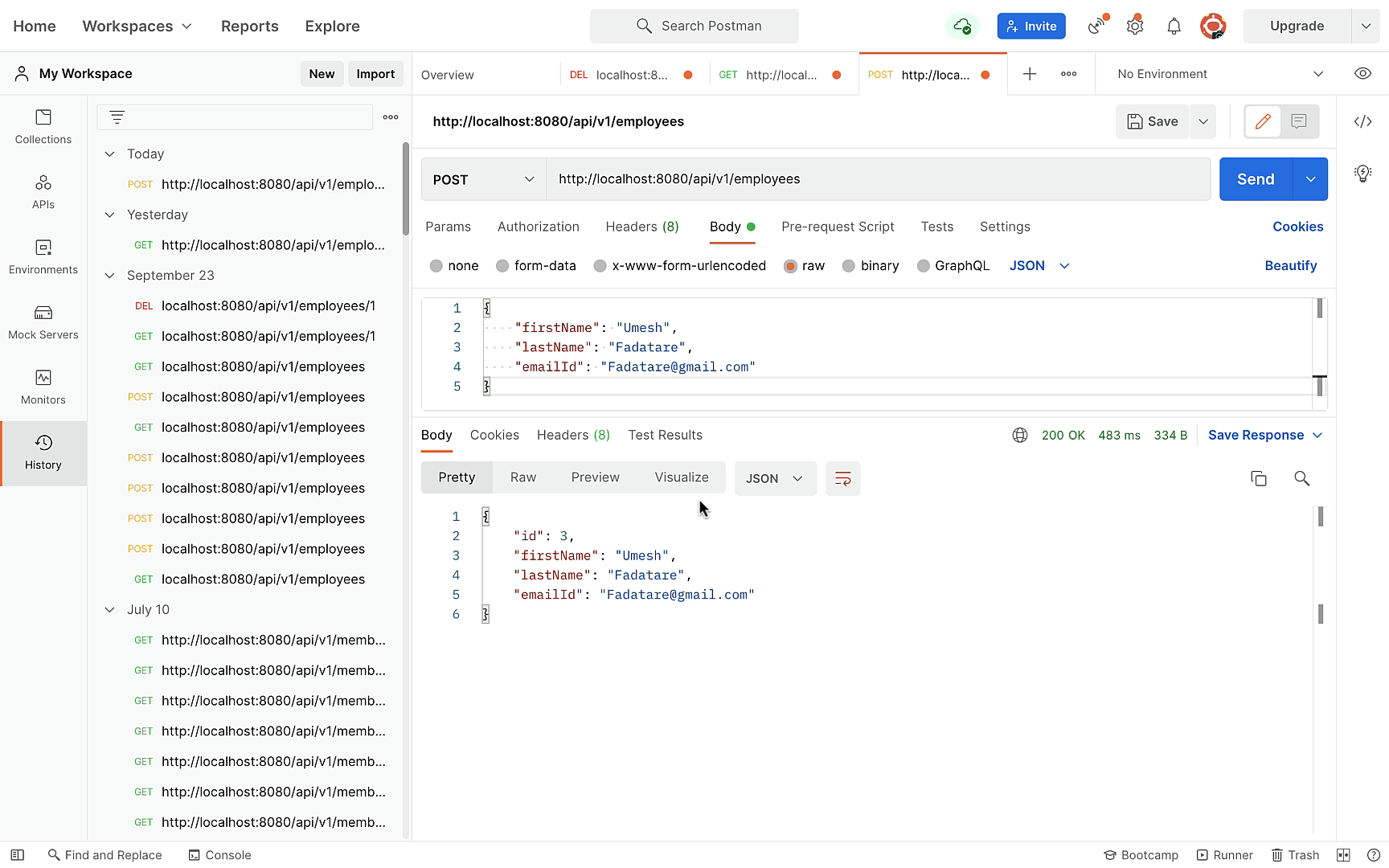
// build create employee REST API
@PostMapping
public Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}Get Employee by Id REST API:
// build get employee by id REST API
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity getEmployeeById(@PathVariable long id){
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id:" + id));
return ResponseEntity.ok(employee);
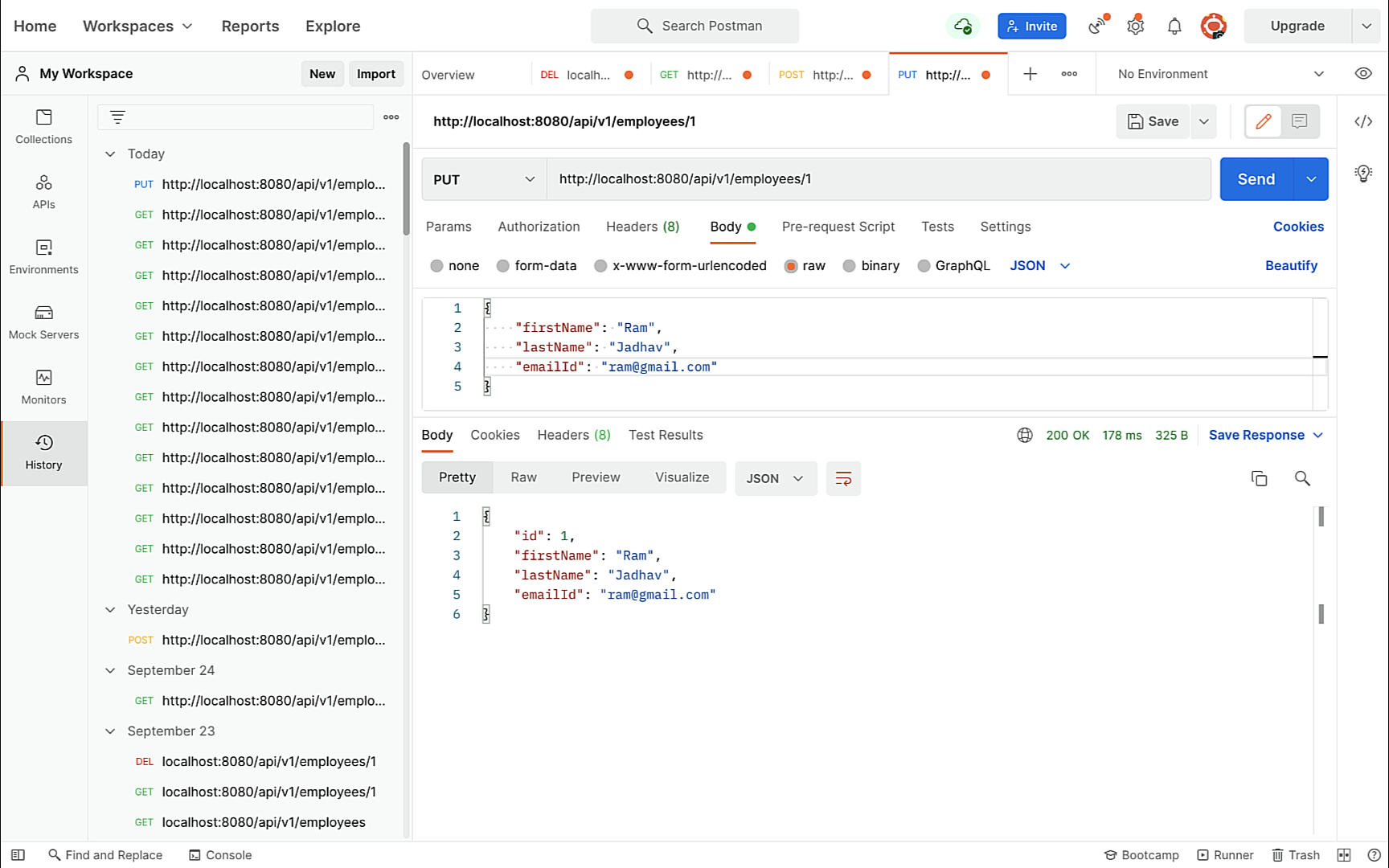
} Update Employee REST API:
// build update employee REST API
@PutMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity updateEmployee(@PathVariable long id,@RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) {
Employee updateEmployee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id: " + id));
updateEmployee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());
updateEmployee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());
updateEmployee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());
employeeRepository.save(updateEmployee);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updateEmployee);
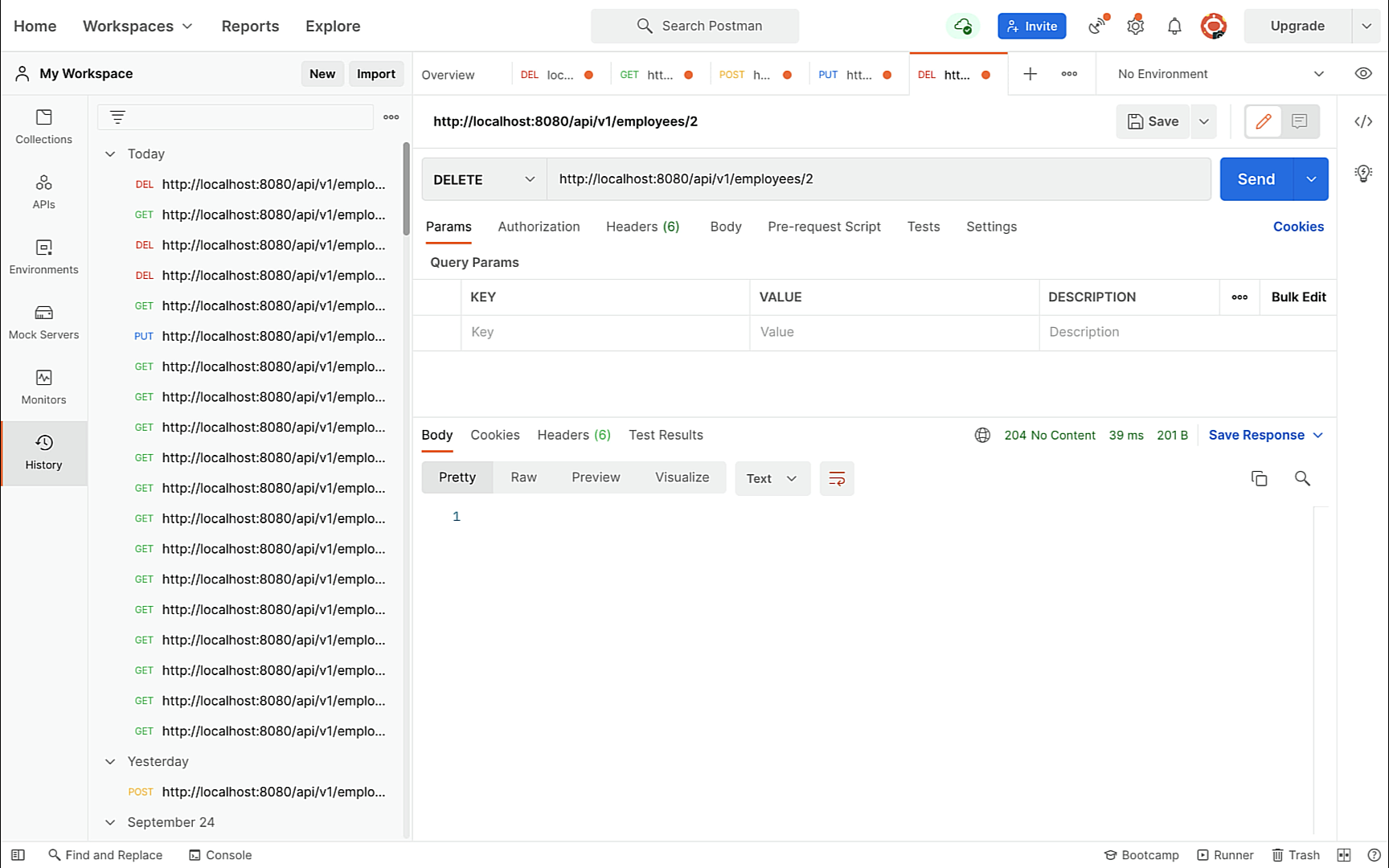
} Delete Employee REST API:
// build delete employee REST API
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity deleteEmployee(@PathVariable long id){
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not exist with id: " + id));
employeeRepository.delete(employee);
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
} We have successfully developed all the CRUD Rest APIs for the Employee model. Now it's time to deploy our
application in a servlet container(embedded tomcat).
Two ways we can start the standalone Spring boot application.
1. From the root directory of the application and type the following command to run it -
$ mvn spring-boot:run
2. From your IDE, run the SpringbootBackendApplication.main() method as a standalone Java class that will start the embedded Tomcat server on port 8080 and point the browser to http://localhost:8080/.
This same tutorial implemented line by line coding in the below YouTube video: